FAQs
We've collated all our frequently asked questions in one place, to make your life easier - you can find everything you need to know here. Contact us if you have any questions.
Filter FAQs
Doors

Aluminium entrance doors are often preferred for their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion and weathering. They can be manufactured with a variety of finishes and colours, allowing for a wide range of customisation options. They are also low-maintenance and easy to clean and can be fitted with energy-efficient glass to improve insulation and reduce heat loss.
Timber entrance doors, on the other hand, offer a more traditional, natural aesthetic that can add warmth and character to your home. They can be crafted in a range of styles and finishes and can be easily repaired or refinished if they become damaged or worn. Timber is also a renewable resource, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Internorm offers both aluminium and timber-aluminium entrance doors in a wide choice of colours, finishes, glass options and accessories. All Internorm front doors offer outstanding thermal performance, making them ideal for Passivhaus projects. They also offer incredible acoustic insulation as well as enhanced security, with Secured by Design and PAS24 accreditation.
Why not have a go at designing your own Internorm entrance door with our clever Door Designer tool?
Create a seamless transition between indoor and outdoor areas with Internorm lift & slide doors. Available in both timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium. They are triple glazed as standard and offer not only incredible thermal performance with U-values as low as 0.64 W/(m2K), making them suitable for Passivhaus project, but also outstanding acoustic insulation and enhanced security hardware.
Ultimately, the choice between lift and slide doors and bi-fold doors will depend on your specific requirements, as well as the design of your home and outdoor space.
Larger glass panels
Lift and slide doors can accommodate larger glass panels than bi-fold doors, which means you can have fewer interruptions in your view and more natural light coming into your home.
Better insulation
Lift and slide doors provide better insulation than bi-fold doors because they have fewer gaps and seams. This can help to reduce energy costs and improve indoor comfort.
Easier operation
Lift and slide doors are generally easier to operate than bi-fold doors because they glide along the track rather than folding and stacking. This makes them a good option for people with limited mobility or for high-traffic areas.
More secure
Lift and slide doors are generally more secure than bi-fold doors because they have a multi-point locking system that engages at multiple points along the track.
Space-saving
Lift and slide doors take up less space than bi-fold doors because they don’t require as much room to open and close. This can be especially important if you have limited space in your home or outdoor area.
Both sliding doors and lift & slide doors are popular options for accessing outdoor areas such as patios or gardens. The main difference between the two is in the way they operate.
A sliding door operates by sliding along a track to open and close. The panels of a sliding door can be quite heavy, which can make them difficult to move for some people. Additionally, sliding doors can be susceptible to air leakage and may not provide as good insulation as other types of doors.
On the other hand, a lift & slide door operates by lifting the door panels off the track before sliding them open or closed. This lifting mechanism allows for much larger and heavier panels to be used, making lift & slide doors a great option for large openings. Additionally, lift & slide doors provide better insulation than sliding doors due to their improved sealing mechanisms.
Lift & slide doors can be a great investment for homeowners looking for a high-quality, high-performance door that provides improved insulation and ease of operation.
All Internorm products feature robust multi-point locking as standard. Options such as i-Tec Secure add further burglary protection, and entrance doors can be fitted with advanced systems like fingerprint recognition.
Internorm offers a wide choice of high-quality materials products, including timber-aluminium composites and uPVC-aluminium composites. Each has unique benefits:
– Timber-aluminium: natural warmth inside, robust protection outside
– uPVC-aluminium: easy care inside, sleek design outside
Internorm windows and doors are available in four distinctive design styles: Studio, Home Pure, Home Soft and Ambiente. You can choose from a wide range of colours, finishes and glazing options to perfectly match your home’s architecture.
Yes. All Internorm products fully comply with, and exceed, UK and European building regulations, including Part L for energy efficiency and security standards such as PAS 24 when specified.
Internorm’s lift-and-slide doors in both timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium are industry-leading for performance and design. They offer expansive openings, triple glazing, and effortless operation, combining panoramic views with superior insulation and security. Combined with fixed glazing or glass-to-glass corners, they can create an even larger glazed opening to maximise views.
Standard sliding doors move on tracks, while lift-and-slide doors, like Internorm’s HS 330 or KS 430, lift slightly before gliding open, creating an airtight seal when closed. This design ensures better insulation, smoother operation, and enhanced weather resistance.
Windows

Air leakage, also known as infiltration or draughts, is the unintentional movement of air into and out of a building through gaps and cracks in the building envelope, including around windows and doors.
In the context of windows, air leakage occurs when outside air is able to enter a building through gaps between the window frame and the building envelope or between the window sash and the frame. Air leakage can have a significant impact on the energy efficiency and comfort of a building, as it can allow cold or hot air to enter the building, making it harder to maintain a consistent indoor temperature. It can also lead to drafts and increased noise levels.
To minimize air leakage, windows should be installed properly and sealed tightly to prevent air from entering or exiting the building. This can be achieved through a combination of high-quality window frames and sashes, effective weatherstripping, and professional installation.
In addition to improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort, reducing air leakage can also help to improve indoor air quality by reducing the infiltration of outdoor pollutants and allergens.
The frame material of windows and doors can have a significant impact on their performance. Here are some ways that different frame materials can affect the performance of windows and doors.
Energy efficiency
The frame material can affect the insulation properties of the window or door. Some materials, such as uPVC or composite frames, are better insulators than others, such as aluminium frames. This can affect the energy efficiency of the window or door, as well as the overall thermal performance of the building. The use of triple gaskets can also hugely improve the performance of a window.
Durability
Different frame materials have different levels of durability and resistance to wear and tear. For example, aluminium frames are very durable and require little maintenance, while wooden frames may require regular maintenance to prevent rot and decay.
Cost
The cost of different frame materials can vary significantly. For example, uPVC frames are typically less expensive than wooden frames or composite frames.
Aesthetics
The frame material can affect the appearance of the window or door and may be an important consideration for some homeowners. Different materials have different finishes and colours available, which can affect the overall look of the window or door.
Environmental impact
The production and disposal of different frame materials can have varying environmental impacts. For example, aluminium frames are often made from recycled materials, while wooden frames are a renewable resource.
Thermal bridging in windows occurs when a conductive material, such as aluminium, is used to connect the glass panes in a window to the window frame. This can provide a path for heat to escape through the window, bypassing the insulating properties of the glass.
Windows are a major source of heat loss in buildings, and thermal bridging in windows can result in increased energy consumption, higher heating bills, and reduced comfort for occupants. To address this issue, manufacturers have developed techniques to reduce thermal bridging in windows.
One common technique is the use of thermal breaks, which are insulating materials placed between two conductive materials to prevent heat transfer. In the case of windows, a thermal break can be installed between the glass and the frame to prevent heat from escaping through the frame.
Another technique is the use of low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings on the glass. These coatings reflect heat back into the room, reducing heat loss through the window. Additionally, triple-glazed windows can be used, which provide an extra layer of insulation between the glass panes, further reducing heat loss through the window.
Overall, reducing thermal bridging in windows is essential for creating energy-efficient buildings and reducing energy consumption. It is important to consider these factors when selecting windows for your building, as well as ensuring that they are installed properly to prevent air leaks and other issues that can lead to heat loss.
Thermal comfort refers to the subjective experience of feeling comfortable in a particular indoor environment. It is influenced by a range of factors, including air temperature, humidity, air movement, and the surrounding surfaces. Windows can play an important role in improving thermal comfort in a building in several ways.
Overall, by choosing high-performance windows and using them strategically, building occupants can enjoy a more comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
Insulation
High-performance windows can help to reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, thereby helping to maintain a more consistent indoor temperature and reducing the need for heating and cooling.
Natural ventilation
Windows can be used to provide natural ventilation, which can help to improve indoor air quality and regulate indoor temperatures. This is especially important in buildings that are not equipped with mechanical ventilation systems.
Daylighting
Windows can also be used to provide natural light, which can help to improve the overall comfort and well-being of building occupants. Exposure to natural light has been linked to improved mood, productivity, and health outcomes.
Views
Finally, windows can provide views of the surrounding environment, which can help to reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
All Internorm products feature robust multi-point locking as standard. Options such as i-Tec Secure add further burglary protection, and entrance doors can be fitted with advanced systems like fingerprint recognition.
Internorm offers a wide choice of high-quality materials products, including timber-aluminium composites and uPVC-aluminium composites. Each has unique benefits:
– Timber-aluminium: natural warmth inside, robust protection outside
– uPVC-aluminium: easy care inside, sleek design outside
Internorm windows and doors are available in four distinctive design styles: Studio, Home Pure, Home Soft and Ambiente. You can choose from a wide range of colours, finishes and glazing options to perfectly match your home’s architecture.
Yes. All Internorm products fully comply with, and exceed, UK and European building regulations, including Part L for energy efficiency and security standards such as PAS 24 when specified.
Internorm triple glazed windows, including timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium can completely transform a coastal home. They provide expansive panoramic views, exceptional thermal and acoustic performance, and a seamless connection between indoor and outdoor living spaces.
Expertly installed by experienced distribution partners, these windows balance aesthetics and functionality, with sleek sight lines, durable finishes, and smooth-operating lift-and-slide doors. Perfect for luxury self-builds or renovations, Internorm glazing enhances natural light, energy efficiency, and the overall comfort of your home. Additionally, we recommend an anodised finish of the external aluminium cladding for coastal properties.
Yes, Internorm offers a number of accessories for its high-performance triple glazed windows and doors. Fly screens are essential for keeping bugs and pollen out of your home, especially during summer months, whilst still allowing fresh air to enter. Essential solar shading is also available to avoid overheating in summer.
Internorm bespoke triple-glazed windows and doors are designed for exceptional energy efficiency and thermal performance, making them perfect for Passivhaus homes. The timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium systems achieve u-values below 0.8 W/(m²K), provide superior airtightness through a triple gasket design, and incorporate insulation within the frame. Together, these features ensure maximum thermal efficiency, durability, and comfort, helping homes meet the strictest energy standards.
Internorm tilt & turn windows offer versatile ventilation and easy cleaning combined with exceptional airtightness and security. The inward-opening design allows precise airflow control without compromising insulation, making them ideal for modern homes where functionality meets architectural elegance.
Internorm composite windows combine the best of both worlds – warm, natural timber or low-maintenance uPVC inside, and durable aluminium outside. This hybrid structure offers superior insulation, strength, and longevity compared to standard uPVC, aluminium or steel systems.
Aluminium-clad windows, such as Internorm’s timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium systems, outperform standard aluminium windows by adding insulation and eliminating thermal bridging. They deliver a warmer interior surface, higher energy efficiency, and a more refined aesthetic.
For newbuilds, Internorm’s HF 410 and KF 520 systems are exceptional. These triple-glazed, highly insulated windows offer contemporary sightlines, passive-level performance, and design flexibility – perfect for architectural projects demanding both efficiency and aesthetics.
The Internorm KF 310 and KF 410 premium alu-clad uPVC ranges are ideal for renovations. They combine slim profiles and triple glazing with advanced security and low-maintenance finishes, enhancing thermal performance without altering existing building aesthetics. If you prefer timber on the inside for some of the living areas, no problem. You can combine Internorm’s uPVC-aluminium and timber-aluminium windows in one project.
Internorm’s KF 410 uPVC-aluminium window is Passivhaus certified, although all Internorm windows and doors are suitable for Passivhaus selfbuild or retrofit projects, achieving U-values below 0.8 W/m²K and exceptional airtightness. Their composite construction and insulated frames ensure maximum energy efficiency, making them the benchmark for sustainable, high-performance homes.
Energy Efficiency
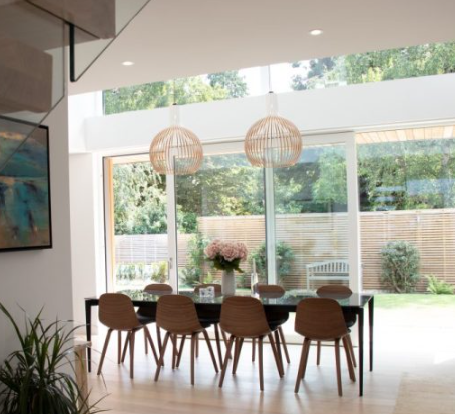

The energy savings between first generation double glazing and triple glazing can be significant, with triple glazing typically providing greater energy efficiency than early double glazing.
First generation double glazing typically had a U-value of around 2.8 W/(m²K), which means that it allowed more heat to escape than modern double glazing or triple glazing. In comparison, high performance triple-glazed windows typically have a U-value of below 1.0 W/(m²K), which can reduce heat loss through windows by up to 80% compared to first generation double glazing. Internorm triple-glazed windows provide outstanding thermal performance as low as 0.62 W/(m²K) and are available in both timber-aluminium composite and uPVC-aluminium. Ideal for Passivhaus and EnerPHit projects, Internorm windows will ensure that your home achieves Passivhaus or EnerPHit certification.
Building regulations changed in June 2022 requiring windows to perform to a higher standard, 1.4 W/(m²K) for renovations and 1.2 W/(m²K) for newbuilds. These figures will reduce in the coming years, so by investing in high-performance, energy-efficient windows and doors now, you will not only save on your energy bills but also future-proof your home.
The exact amount of energy savings between first generation double glazing and triple glazing will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific properties of the windows and the local climate. However, it is generally accepted that triple glazing is more energy efficient than first generation double glazing and can provide greater levels of thermal comfort, sound insulation, and air tightness.
EnerPHit is a certification for retrofit projects that aims to improve the energy efficiency of existing buildings to a very high standard. It is a quality assurance scheme developed by the Passivhaus Institute, which is based in Germany and is a world-renowned authority on low-energy buildings.
EnerPHit certification requires that buildings meet the same rigorous energy efficiency standards as new buildings certified under the Passivhaus standard, but with more flexibility to account for the limitations of retrofitting existing buildings. EnerPHit certification includes strict requirements for airtightness, insulation, and mechanical ventilation, as well as measures to minimize thermal bridging and control solar gains.
EnerPHit certification is often sought by building owners and designers who want to improve the energy efficiency and comfort of existing buildings, while also reducing their environmental impact and energy costs. It is particularly relevant for retrofit projects in colder climates, where heating demands can be significant.
Internorm triple-glazed windows and doors are ideally suited for EnerPHit projects. Offering outstanding thermal performance with U-values as low as 0.62 W(m2K), Internorm products have been used for both EnerPHit and Passivhaus certified domestic and commercial buildings, including offices, schools, and care homes.
Internorm also offers shading solutions that can be incorporated into an EnerPHit project, from accessible integrated blinds, available with both timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium windows and doors, as well as Raffstore external venetian blinds, which are ideal for larger glazing, including triple-glazed lift & slide doors.
Internorm products achieve some of the best U-values on the market, making them suitable even for Passivhaus projects. All Internorm products are triple glazed as standard, helping to reduce energy consumption and create a comfortable home environment.
Sustainability is a core principle at Internorm. We use responsibly sourced timber, energy-efficient production processes and recyclable materials. Our Austrian factories are among the most advanced in Europe for reducing waste, water use and carbon emissions.
Internorm bespoke triple-glazed windows and doors are engineered for maximum energy efficiency. With u-values under 0.8 W/(m²K), a triple gasket design, and built-in frame insulation, these timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium systems ensure outstanding thermal performance and airtightness for Passivhaus and low-energy homes.
Blinds

Yes, external blinds are generally more effective than internal blinds in reducing solar gain.
This is because external blinds can block the sun’s rays before they reach the glass, preventing the heat from entering the room. In contrast, internal blinds can only block the sunlight after it has entered the room and has already contributed to the heating of the space.
External blinds also have the added advantage of shading the glass, which can help to reduce the amount of heat that is radiated into the room. Additionally, external blinds can be more durable and require less maintenance compared to internal blinds.
However, external blinds can be more expensive and may require professional installation, while internal blinds can be more cost-effective and easier to install.
When buying windows and doors, you should always consider shading, especially on south and south-west facing elevations, to avoid overheating. Nobody wants to feel like they are living in a glasshouse during the summer.
Raffstore Venetian blinds
External blinds that are ideal for larger areas of glazing, including Internorm lift & slide doors, as well as windows.
Integrated blinds
The difference between conventional integrated blinds and the integrated blinds in Internorm’s HV 450 and KV 440/ KV 350 windows is that the blind is fully accessible.
Choose from Venetian, Roman and Duette® blinds in a range of colour options, these blinds are protected from wind, dirt, and dust by being fully integrated between accessible glass. panes. Available hard-wired, with manual ball-chain operation or with Internorm’s unique I-tec Shading. I-tec Shading offers operation of the blinds via a photovoltaic module using solar energy, therefore not requiring an external power source.
Internal blinds
Also available for Internorm uPVC-aluminium and timber-aluminium windows.
i-Tec is Internorm’s exclusive range of smart technologies, which includes features such as integrated blinds, glazing, locking and shading. These innovations improve security, comfort and energy efficiency while maintaining a sleek design.
To keep your home cool and avoid overheating during the summer months, it is essential to include shading, and in particular external shading, to your windows and large lift & slide doors. Internorm offers durable external Raffstore aluminium blinds, as well as the unique, accessible integrated blinds. These are also available as I-tec Shading, where the integrated blinds are operated via a PV panel, are powered by the sun, and do not require hard wiring.
Solar Energy

In the context of windows and glazing, the g-value refers to the total solar energy transmittance through a window. Specifically, it represents the percentage of total solar energy (including both visible and invisible radiation) that passes through the glazing and enters the building.
The g-value is an important measure of the performance of a window, as it can affect the amount of heat gain that occurs in a building. In hotter climates, windows with a lower g-value are generally preferred, as they allow less solar heat to enter the building and can help to keep it cooler. In cooler climates, windows with a higher g-value may be preferred, as they can help to bring in more solar heat and reduce heating costs.
The g-value is typically measured using a spectrophotometer, which can measure the percentage of solar energy transmitted through the glazing at different wavelengths. It is important to note that the g-value is just one factor to consider when choosing windows, and other factors such as U-value and air leakage should also be taken into account to ensure the best possible performance.
Solar gain refers to the heat gained from the sun’s rays that enter a building through its windows, walls, or roof. The amount of solar gain depends on the orientation of the building, the size and number of windows, and the type of glazing used.
To maximise the benefits of solar gain and minimise the problems, building design should take into account factors such as the orientation of the building, the size and location of windows, and the use of shading devices and glazing materials that help control the amount of solar gain.
Reduced energy costs
In colder climates, solar gain can help reduce the need for heating, while in warmer climates, it can help reduce the need for cooling. This can lead to lower energy bills and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Improved comfort
Solar gain can provide natural warmth and light, making a space feel more comfortable and inviting.
Health benefits
Exposure to natural light has been linked to improved mental health, while exposure to natural warmth can help relieve symptoms of conditions such as arthritis.
Overheating
Excessive solar gain can lead to overheating, which can make a space uncomfortable and even dangerous. This can be particularly problematic in buildings without proper ventilation or shading.
Fading
Solar gain can cause furniture, fabrics, and artwork to fade over time, due to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
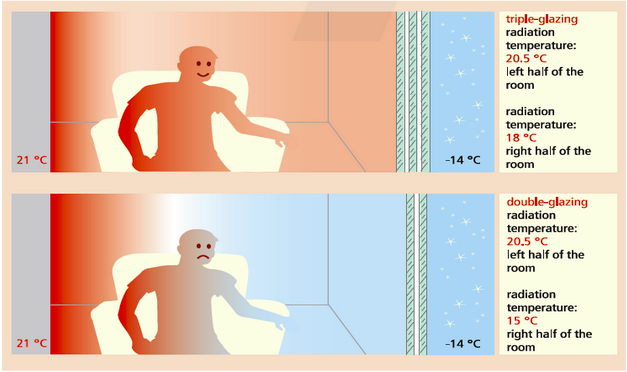
Triple Glazing

Triple glazing can improve acoustic performance compared to double glazing. The extra pane of glass and the insulating layers of gas between the glass panes in triple glazing help to reduce the transmission of sound waves through the windows, resulting in improved acoustic insulation.
The ability of a window to reduce noise is measured by its sound reduction index (SRI), which is expressed in decibels (dB). A higher SRI means that the window provides better sound insulation. Triple glazing typically has a higher SRI than double glazing, as it provides an additional barrier to block sound waves.
The effectiveness of triple glazing in reducing noise transmission depends on several factors, such as the thickness of the glass panes, the distance between the panes, and the type of gas used to fill the space between the panes. A well-designed triple glazing unit can provide significant noise reduction, making it an excellent choice for buildings located in noisy environments, such as near busy roads or airports.
Yes, Internorm products are supplied with triple glazing as standard. This ensures excellent thermal insulation, noise reduction and enhanced security.
Coastal properties quite often have to withstand extreme weather conditions. Internorm triple glazing improves thermal efficiency and air tightness due to its triple gasket construction. Internorm high-performance triple glazed windows and doors also offer outstanding noise reduction and enhances security, making them perfect for homes with large glazed areas or in challenging coastal environments. The external powder-coated aluminium can be anodised for coastal homes to avoid corrosion, therefore making Internorm triple-glazed windows some of the best windows and doors for seaside properties.
Absolutely! The Internorm product range has been used successfully in Passivhaus projects for many years. In fact, they are the go-to windows and doors for Passivhaus self-bullds, low-energy and Eco Homes, as well as retrofits due to their outstanding quality, thermal efficiency, insulated frames, air tightness and durability, making them the ideal solution for anyone looking to create a sustainable Passivhaus home.
Internorm triple-glazed windows and doors combine timber-aluminium or uPVC-aluminium construction with integrated frame insulation and a triple gasket system. Achieving u-values below 0.8 W/(m²K) and exceptional airtightness, they provide high thermal efficiency, helping Passivhaus projects meet strict energy standards.
Internorm triple-glazed windows and doors deliver top-tier thermal efficiency and airtightness. Their timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium designs include triple gaskets and insulated frames, achieving u-values below 0.8 W/(m²K). This makes them ideal for energy-efficient Passivhaus homes requiring long-term comfort and low heat loss. Together with essential external shading solutions, Internorm offers the most complete product range for Passivhaus and EnerPHit projects.
Yes, although you need to do your homework, as not all triple glazing is the same in quality and performance. Triple glazed windows offer significantly higher thermal efficiency, improved acoustic insulation, and enhanced comfort compared to double glazing. Internorm’s triple-glazed system was introduced as early as 1979, so it’s nothing new.
Internorm high-performance triple glazed windows and doors are made from premium components, raw materials, and hardware. Combined with triple gaskets, insulated frames, as well as all-round bonded glazing, these timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium products minimise heat loss and condensation, creating a quieter, warmer, and more energy-efficient living environment.
Absolutely. While the initial cost is higher, Internorm triple glazing delivers measurable long-term savings through reduced heating demand and lower energy bills. Combined with improved home comfort, durability, and property value, it’s an investment in both performance and peace of mind.
The payback period varies by home size and insulation, but Internorm triple-glazed windows typically offset their cost within 5–10 years through lower energy consumption. Their long lifespan and minimal maintenance make them one of the most cost-effective upgrades for energy and sustainability-conscious homeowners.
Upgrading to Internorm’s triple-glazed windows can reduce annual heating costs by up to 50%, sometimes more, depending on property type and insulation levels. With U-values below 0.8 W/(m²K) and airtight, insulated frame construction, Internorm windows retain more heat, cutting both energy bills and carbon emissions, making them a sustainable solution for selfbuild, renovation, and Passivhaus projects.
The best triple-glazed window combines energy efficiency, aesthetics, and precision engineering- qualities that define Internorm’s timber-aluminium and uPVC-aluminium systems. Models like the HF 410 and KF 520 achieve ultra-low U-values, sleek design lines, and exceptional performance for both contemporary and traditional architecture.
Popular for Passivhaus selfbuilds and retrofits, the Internorm alu-clad high-performance product range also includes essential external shading solutions to avoid over-heating during summer months, as well as fly screens to keep bugs out. In addition to tilt & turn windows, Internorm offers large lift & slide doors, Panorama fixed glazing, glass-to-glass corners, entrance doors, as well as Juliette balconies.
Quality varies widely between manufacturers. Internorm windows are engineered in Austria to exacting standards, offering consistent airtightness, superior materials, and longevity proven over decades. Many lower-cost alternatives lack this precision manufacturing and insulation technology, leading to reduced efficiency and durability.
Prices & Installation

Internorm is a family-owned business founded in 1931 in Austria. Over more than 90 years, it has grown into Europe’s leading window brand, still managed by the founding family today.
All Internorm windows and doors are manufactured in Austria at three state-of-the-art production facilities. This allows us to maintain strict quality control, innovation and sustainability standards. Internorm owns its own uPVC extrusion and glass facility to ensure the highest quality and consistency for all its products.
Internorm windows and doors are backed by extensive warranties, including a 10-year guarantee on the frame construction, 10 years on colourfastness for aluminium surfaces and 5 years on insulating glass. Full details are available from your local Distribution Partner.
You can locate your nearest Internorm Distribution Partner using our Partner Finder tool on the website. Our partners are carefully selected to deliver expert advice, professional installation and outstanding after-sales support.
Lead times vary depending on the product range and customisation options. On average, delivery takes 8–12 weeks from order confirmation, with installation time depending on the scale of your project. Your Distribution Partner will provide a tailored schedule.
Our Distribution Partners provide full after-sales support, including maintenance advice, adjustments and access to spare parts. Internorm also ensures long-term product availability, so components can be replaced or upgraded if needed, and the Internorm UK Service Department is available for any service-related concerns. Please email: service@internorm.com, if you require assistance.
Internorm products are independently tested and certified for performance, including Secured by Design and Passivhaus accreditation. We have also received international design awards such as the Red Dot Award, reflecting both technical excellence and aesthetic quality.
Supply-only means you purchase Internorm products through some, but not all, Distribution Partner but arrange installation separately. With supply & install, the same trusted partner manages the full process, ensuring expert fitting and warranty protection, which is our recommendation to ensure your Internorm products perform to the highest standards and warranties are valid.
Standard lead times are usually 8–12 weeks, depending on the product, glazing and finish options chosen. Larger or more complex projects may take a little longer, and your Distribution Partner will provide an accurate timeframe at quotation.
Internorm products are fully bespoke and manufactured to your individual requirements. Prices depend on several factors, including product type, dimensions, frame material, glazing choice and optional features. Your Distribution Partner will prepare a tailored quotation after a consultation, ensuring your solution meets both budget and design goals.
Yes, they can but there naturally are limitations. With their slim sightlines, timber finishes and traditional design options, including glazing bars, Internorm products can meet the requirements of conservation officers. We recommend consulting both your architect and local authority before proceeding.
Internorm windows and doors are extremely versatile and can be used in a wide variety of projects, from modern new-builds and Passivhaus homes to traditional renovations. With four design styles and custom finishes, they can be tailored to suit contemporary, classic, urban or rural architecture. Essential shading solutions, fly screens and stylish entrance doors are also available.